In the high-stakes world of military radar systems, ensuring the reliability and performance of every component is critical. One key aspect that often goes under the radar is PCB traceability standards. But what exactly are the traceability requirements for military radar printed circuit boards (PCBs)? Simply put, traceability in this context means the ability to track every component, material, and manufacturing process involved in creating a PCB, ensuring quality, compliance, and accountability at every step. This blog dives deep into the importance of component tracking PCB, manufacturing data PCB management, quality control military standards, and the role of serialized PCB in meeting stringent military demands.
Whether you're an engineer, a procurement specialist, or a manufacturer working on defense projects, understanding these requirements is essential for delivering reliable and compliant radar systems. Let's explore the intricacies of traceability for military radar PCBs, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.
What Is PCB Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Military Radar?
PCB traceability refers to the systematic process of recording and tracking every detail of a printed circuit board's lifecycle—from raw materials to final assembly and deployment. In military radar applications, where systems must operate flawlessly under extreme conditions, traceability is not just a best practice; it's a strict requirement. A single failure in a radar system could compromise national security or endanger lives, making it vital to pinpoint the source of any issue quickly.
Traceability ensures accountability by documenting the origin of components, the manufacturing steps, and even the environmental conditions during production. For military radar PCBs, this means adhering to rigorous standards set by organizations like the Department of Defense (DoD) and industry bodies such as the Institute of Printed Circuits (IPC). These standards often fall under classifications like IPC Class 3, which demands the highest level of reliability for life-critical systems.

Key Traceability Requirements for Military Radar PCBs
Military radar PCBs are subject to unique challenges, including high-frequency signal integrity (often in the range of 1 GHz to 77 GHz for modern systems), extreme thermal conditions, and exposure to harsh environments. Meeting traceability requirements ensures these boards can withstand such demands. Below are the core elements of traceability for military radar PCBs.
1. Component Tracking PCB: Ensuring Every Part Is Accountable
Every component on a military radar PCB, from resistors to high-frequency RF connectors, must be traceable to its source. This process, known as component tracking PCB, involves documenting the manufacturer, batch number, and even the date of production for each part. In military applications, components must often meet strict specifications, such as MIL-PRF (Military Performance Specification) standards, to ensure they can handle extreme conditions.
For example, a capacitor used in a radar PCB might need to operate reliably at temperatures ranging from -55°C to 125°C. If a failure occurs, traceability allows engineers to identify whether the issue stems from a specific batch of capacitors or a supplier's quality lapse. This level of detail is crucial for root cause analysis and preventing future failures.
2. Manufacturing Data PCB: Documenting Every Step
The production of military radar PCBs generates a vast amount of data, often referred to as manufacturing data PCB. This includes information on fabrication processes, assembly techniques, soldering methods, and testing results. Every step must be logged to ensure compliance with military standards and to provide a clear audit trail.
For instance, during the fabrication of a multilayer PCB for radar, the lamination process must maintain precise impedance control (often within ±10% of the target value, such as 50 ohms for RF lines). Manufacturing data logs these parameters, along with details like the type of dielectric material used (e.g., Rogers RO4350B for high-frequency applications) and the curing temperatures. This data is invaluable for troubleshooting and verifying compliance with military specs.

3. Quality Control Military: Meeting Stringent Standards
Quality control military standards are non-negotiable for radar PCBs. Military systems often require adherence to standards like MIL-STD-810 for environmental testing and MIL-PRF-31032 for PCB fabrication. Traceability plays a central role in quality control by ensuring every PCB meets these criteria through documented testing and inspection processes.
For example, a military radar PCB might undergo thermal cycling tests to simulate temperature swings from -40°C to 85°C over 1,000 cycles. Traceability records confirm that these tests were conducted, along with pass/fail results and any deviations observed. This level of scrutiny ensures that only the highest-quality boards make it into critical defense systems.
4. Serialized PCB: Unique Identification for Accountability
A serialized PCB is one that carries a unique identifier, such as a barcode or QR code, etched or printed onto the board. Serialization is a cornerstone of traceability, allowing manufacturers to track individual PCBs through the supply chain and into the field. For military radar systems, serialization ensures that a specific board can be linked to its production records, test results, and deployment history.
Serialization is particularly useful during maintenance or failure analysis. If a radar system malfunctions during a mission, the serialized identifier on the PCB can be used to retrieve its entire history, from the components used to the environmental conditions it endured during assembly. This speeds up diagnostics and ensures accountability at every stage.
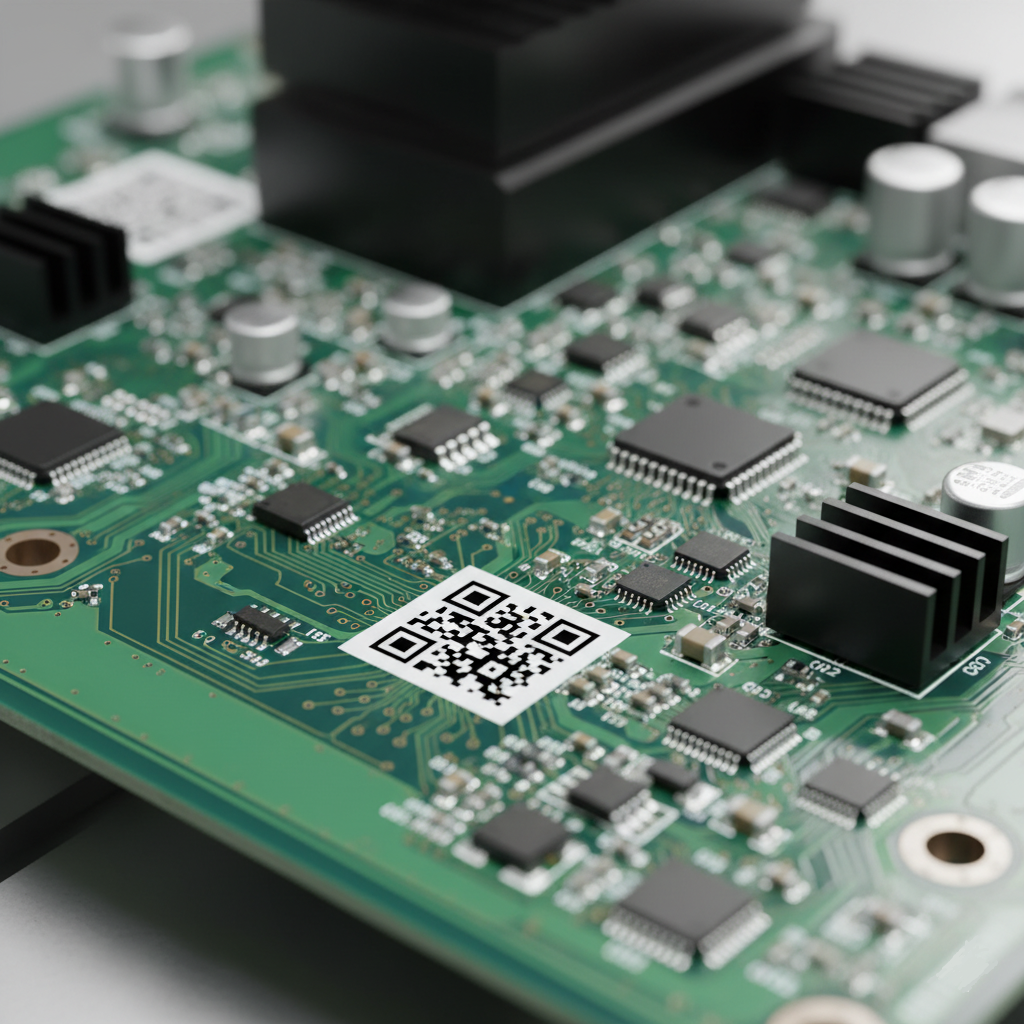
Challenges in Implementing Traceability for Military Radar PCBs
While the benefits of traceability are clear, implementing it for military radar PCBs comes with significant challenges. These include the complexity of supply chains, the need for secure data management, and the high cost of compliance.
First, military radar PCBs often rely on components sourced from multiple suppliers across the globe. Tracking every part's origin and ensuring it meets military standards can be a logistical nightmare. Advanced software systems and blockchain technology are increasingly used to create tamper-proof records of component provenance, but these solutions require investment and expertise.
Second, the sensitive nature of military projects demands strict data security. Manufacturing data and traceability records must be protected from unauthorized access or tampering. This often means implementing encrypted databases and restricted access protocols, adding another layer of complexity.
Finally, the cost of maintaining detailed traceability records can be substantial. For instance, testing a single PCB for signal integrity at high frequencies (e.g., ensuring minimal insertion loss below 3 dB at 10 GHz) requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. Documenting these tests in detail adds to the overall expense but is non-negotiable for military applications.
Best Practices for Achieving Traceability in Military Radar PCBs
Despite the challenges, manufacturers can adopt several best practices to meet PCB traceability standards for military radar systems. These strategies ensure compliance while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
1. Adopt Digital Traceability Systems
Modern traceability relies heavily on digital tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). These platforms automate the collection of manufacturing data PCB and integrate it with component tracking, making it easier to maintain comprehensive records. For example, an MES can log real-time data on soldering temperatures (typically around 260°C for lead-free processes) and correlate it with specific PCB batches.
2. Implement Robust Serialization Methods
Using durable and tamper-proof serialization techniques, such as laser etching for serialized PCB identifiers, ensures that traceability remains intact even under harsh conditions. Military radar PCBs often operate in environments with high vibration or moisture, so the serialization method must withstand these factors without degrading.
3. Partner with Compliant Suppliers
Ensuring component tracking PCB starts with working with suppliers who adhere to military standards. Requesting certificates of conformance (CoC) and material test reports (MTR) for every component batch helps verify quality and origin, reducing the risk of counterfeit or substandard parts entering the supply chain.
4. Conduct Regular Audits for Quality Control Military
Regular internal and third-party audits of traceability processes ensure that quality control military standards are consistently met. Audits should review documentation practices, test results, and data security measures to identify gaps and implement corrective actions promptly.

The Future of Traceability in Military Radar PCBs
As military radar technology evolves, so do the demands for traceability. Emerging trends like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) are poised to revolutionize how traceability data is collected and analyzed. IoT-enabled sensors on manufacturing equipment can provide real-time data on parameters like humidity (maintained below 50% RH in cleanrooms) or pressure during PCB lamination, enhancing the granularity of traceability records.
AI, on the other hand, can analyze vast datasets to predict potential failure points based on historical traceability data. For instance, if a specific batch of dielectric material consistently shows deviations in dielectric constant (e.g., varying from 3.5 to 3.7), AI algorithms can flag it before it affects radar performance.
Additionally, stricter regulations around cybersecurity will likely shape the future of traceability. Military projects may require blockchain-based systems to create immutable records of manufacturing data PCB, ensuring data integrity even in the face of cyber threats.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Traceability for Military Radar Success
Traceability is the backbone of reliability for military radar PCBs. By adhering to PCB traceability standards, implementing robust component tracking PCB processes, managing manufacturing data PCB effectively, enforcing quality control military measures, and leveraging serialized PCB techniques, manufacturers can ensure that every board meets the stringent demands of defense applications.
The road to achieving full traceability is not without challenges, but with the right tools, partnerships, and practices, it's an achievable goal. As technology advances, staying ahead of traceability requirements will be key to delivering radar systems that protect and perform when it matters most. For engineers and manufacturers in the defense sector, prioritizing traceability isn't just about compliance—it's about building trust and ensuring mission success.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB