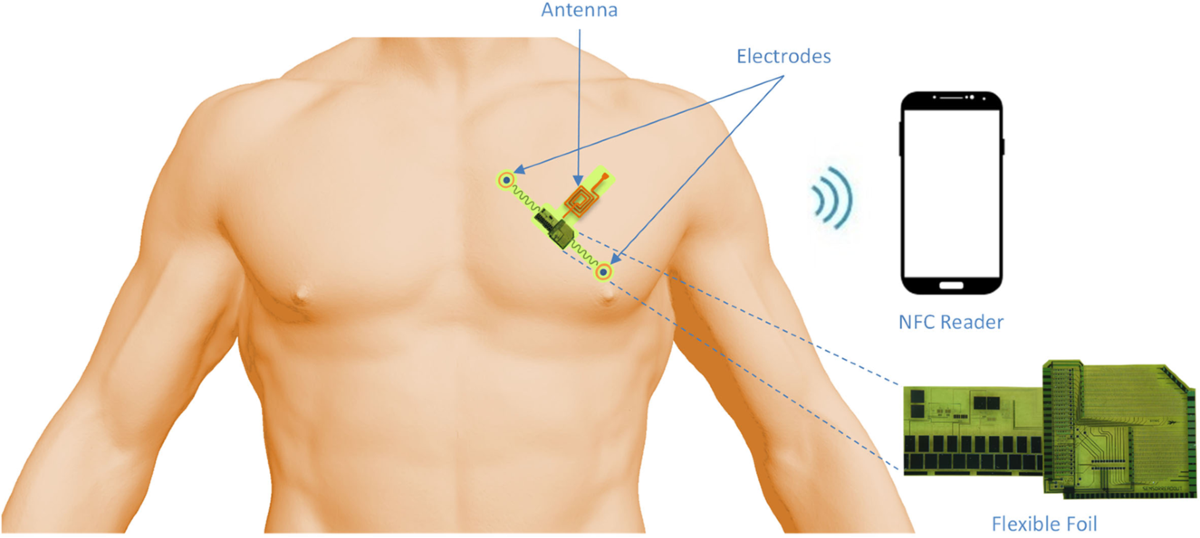
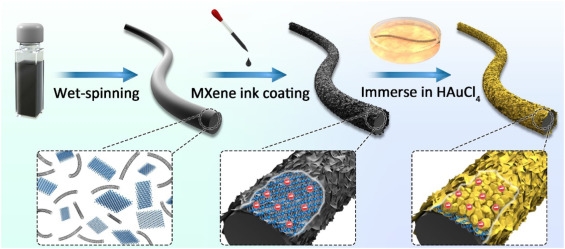
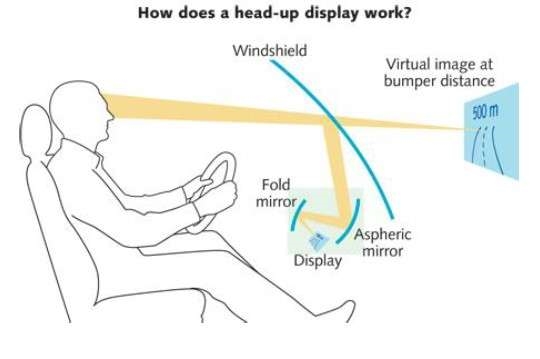
Overview
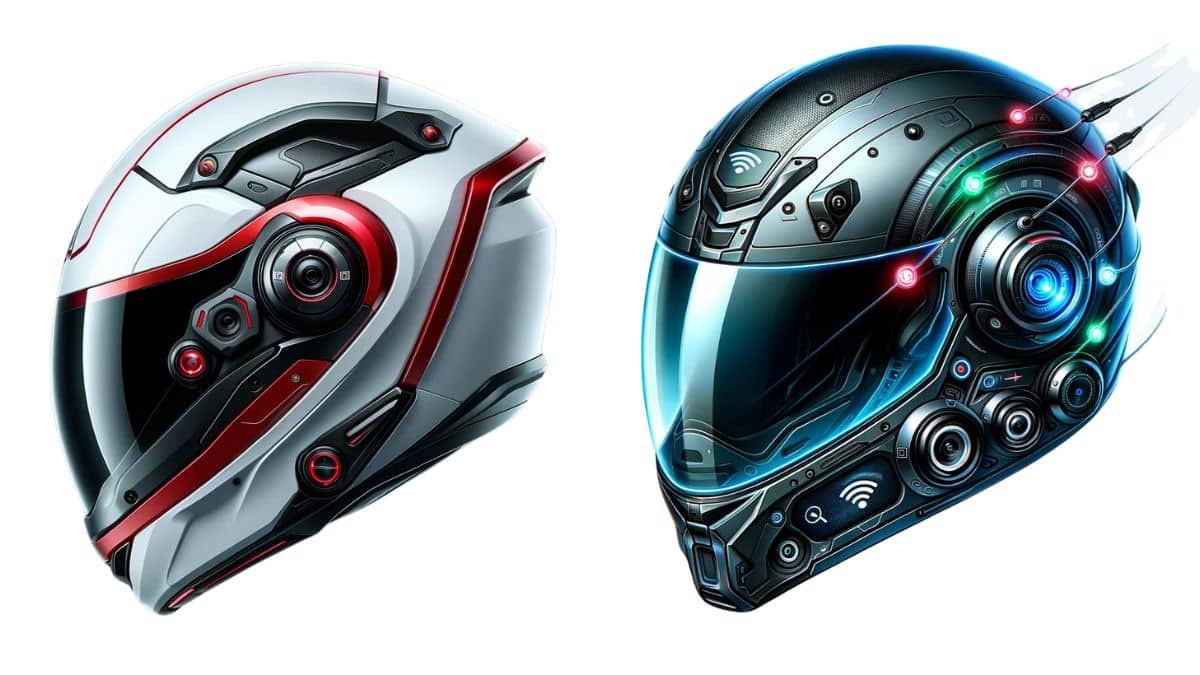
A smart helmet is a wearable device that integrates multiple technologies and functions. By incorporating sensors, displays, audio devices, communication modules, and other components, it delivers a variety of capabilities. Common features and uses include:
Common Features and Uses
- Augmented reality (AR): Smart helmets can overlay virtual information onto the real world via a display, enabling immersive interactions, navigation, and gaming.
- Head tracking and posture recognition: Built-in sensors track head movement and posture to provide more natural, interactive experiences in virtual reality and gaming applications.
- Video and audio playback: Smart helmets often support video and audio playback through integrated displays and headphones or speakers, allowing users to consume multimedia or training materials on the go.
- Communication and connectivity: Typical wireless technologies include Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, enabling connection with other devices such as smartphones and computers for data transfer and notifications.
- Real-time navigation and information display: Navigation systems and map applications can present turn-by-turn directions and location information in the user’s field of view via displays or projection.
- Safety protection and monitoring: Some smart helmets include features for monitoring user health, posture detection, and alerting, which can enhance safety and convenience.
Key Technologies Used
Smart helmets combine several core technologies to realize their functions, including:
- Virtual reality (VR): Widely used in VR applications, smart helmets use high-resolution displays, sensors, and tracking systems to immerse users in 3D virtual environments.
- Augmented reality (AR): AR uses cameras, sensors, and displays to overlay virtual images or data onto the real world, allowing simultaneous perception of virtual and real elements.
- Head tracking: Gyroscopes, accelerometers, and other sensors detect head motion and orientation, providing real-time feedback to control virtual viewpoints or in-system interactions.
- Human-computer interaction (HCI): Interaction methods include touch controls, voice recognition, and gesture recognition, enabling control through simple actions or spoken commands.
- Wireless communication: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enable data exchange with external devices for receiving information or sending commands.
- High-definition displays: Helmet displays typically offer high resolution, high refresh rate, and wide viewing angles to deliver clear, smooth, and realistic visuals.
Outlook
Development of smart helmets continues, and future applications may expand into areas such as virtual reality gaming, healthcare, and industrial maintenance. Privacy protection and safety remain important considerations to ensure lawful and reliable use.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB