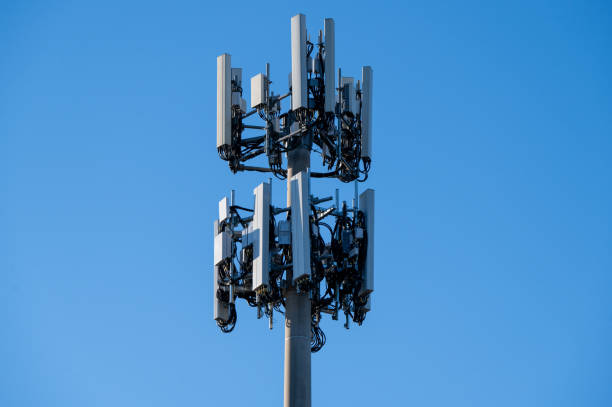
Base station components
A base station is a key element of a wireless communication network that provides radio coverage and data transport services. A typical base station consists of three main parts:
- Antenna: The antenna transmits and receives radio signals. It radiates signals into the surrounding area to serve user devices and receives signals sent by user devices. Antenna type and configuration depend on the radio technology and network design.
- Wireless transceiver: The transceiver is the core radio element that communicates with user devices. It includes radio frequency (RF) modules that convert between radio and electrical signals, and signal processors that perform encoding, decoding, and other signal processing functions to manage transmission.
- Base station controller: The controller is the control unit that manages base station operation. It allocates and schedules radio resources, controls link setup and maintenance, handles data forwarding, and coordinates with the core network.
Functions of mobile base stations
Mobile base stations perform several essential functions in a wireless network:
- Radio coverage: Provide wide-area radio coverage so user devices can communicate within the service area.
- Signal conversion: Convert signals between the radio domain and electrical domain so user devices can connect to the network.
- Data transport: Handle data transfer between user devices, managing and forwarding traffic to ensure stable transmission.
- Management and control: Manage radio resource allocation, control operational state, and interact with the core network for authentication, call control, and other functions.
- Service support: Enable mobile services such as voice, messaging, and data access by providing the connection point between users and network services.
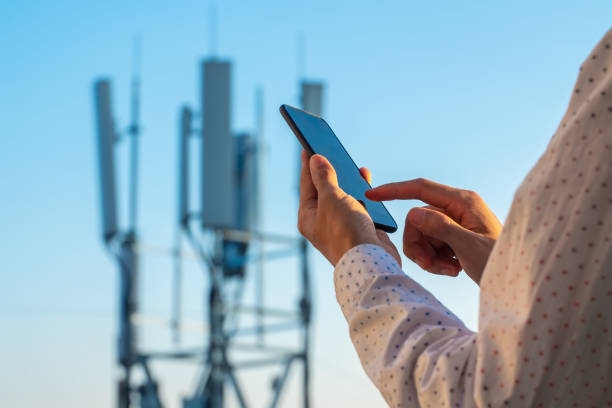
Does radiation increase when closer to a base station?
In general, the received electromagnetic field strength is higher closer to a base station antenna. Radio signals from a base station propagate through space and are subject to path loss, attenuation, and scattering. As distance from the antenna decreases, the received power density typically increases.
However, base stations and user devices use power control. When a user device is far from the site, higher transmit power may be required to maintain signal quality; when the device is close, the required transmit power is reduced. Therefore, proximity to a base station does not automatically imply higher transmitted power from the network or a greater health risk.
Regulatory bodies and international guidelines exist for spectrum management and radiation safety. Base stations are designed and operated to comply with these standards to ensure that exposure levels remain within internationally accepted limits. For additional precaution, users can maintain reasonable distance from base station equipment and use wireless devices that meet recognized safety standards.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB