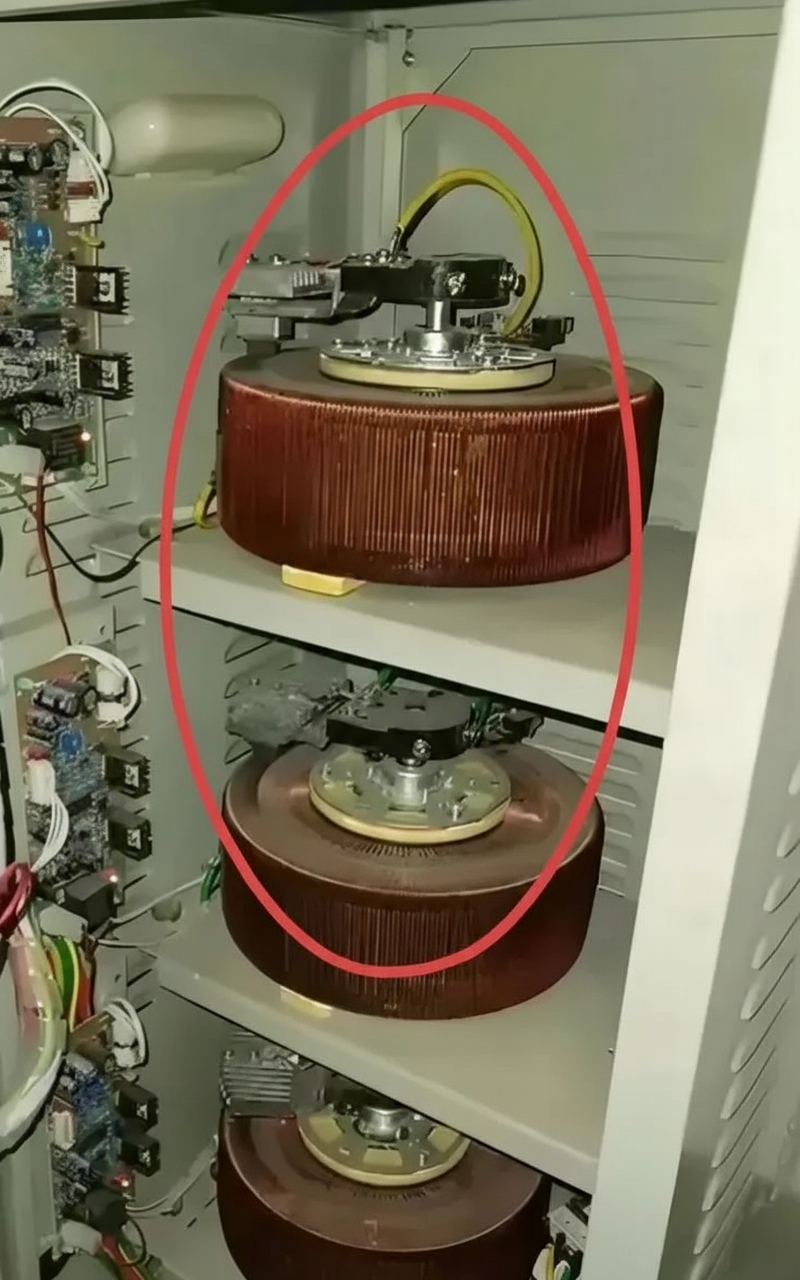
An image showing three circular discs inside a distribution cabinet prompted investigation. After reviewing technical materials and peer commentary, the three discs were identified as a three-phase autotransformer used for voltage regulation. It is installed where AC supply voltage is unstable to keep the voltage within rated limits and ensure connected equipment operates normally.
What is a three-phase autotransformer
A three-phase autotransformer is a type of autotransformer with winding configurations equivalent to those of a conventional three-phase transformer, but with electrically common windings. It is mainly used in high-power transmission and transformation applications.
Working principle
When the three-phase AC supply current passes through the input winding of the autotransformer, it produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field links the common winding and induces voltage in the output winding. If the common winding has more turns than the output winding, the output voltage will be higher than the input voltage.
In an autotransformer, the input and output windings are connected via a shared winding, so there is electromagnetic coupling between them. This coupling enables voltage conversion. When the input voltage changes, the output voltage changes proportionally according to the turns ratio between the input and output windings.
Autotransformers offer advantages such as smaller size, lighter weight, and higher efficiency, and are widely used in power systems. They are applied in voltage conversion, voltage regulation, and power transmission. By designing the turns ratio appropriately, autotransformers can convert between different voltage levels to meet the requirements of various power equipment.
Structural features
An autotransformer is a single-coil transformer in which the primary and secondary share the same winding, giving it a fixed transformation ratio. Compared with a conventional transformer of the same capacity, it has a simpler structure, uses less material, and occupies less space. It is particularly economical when the turns ratio is close to 1, so it is often used in large-capacity transmission transformers where voltages are similar. It is also widely used in reduced-voltage starting boxes for induction motors above 10 kW.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB