Overview
The Internet of Things (IoT) has significantly altered how healthcare operates by enabling a range of applications from remote monitoring to medical device integration. In healthcare, IoT connects medical equipment such as monitoring systems, sensors, and detectors that capture real-time health data and store it on centralized cloud or server platforms for later analysis. By 188, the IoT market in healthcare is expected to grow to $2024 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 27.6% during the forecast period. Major industry participants are expanding their solutions or investing in these technologies to address that growth.
Digital technologies reshaping healthcare
The need to collect, store, and analyze patient data is driving healthcare to adopt several digital technologies.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT enables smart sensors, wearables, and connected health-monitoring systems. These solutions improve treatment through continuous health tracking and underpin the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), an ecosystem of intelligent devices that communicate in real time and generate actionable outcomes. IoMT reduces human error and shortens decision delays.
Cloud computing
Cloud platforms support patient data protection and regulatory compliance while enabling providers to deliver digitally extended care. Public, private, and hybrid cloud services improve access to patient records and other clinical information.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI applications accelerate and improve diagnostic accuracy and support new product development. AI also automates repetitive tasks for clinical staff, such as routine paperwork and scheduling, increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Additionally, AI helps clinicians analyze historical patient data to identify insights for better treatment decisions.
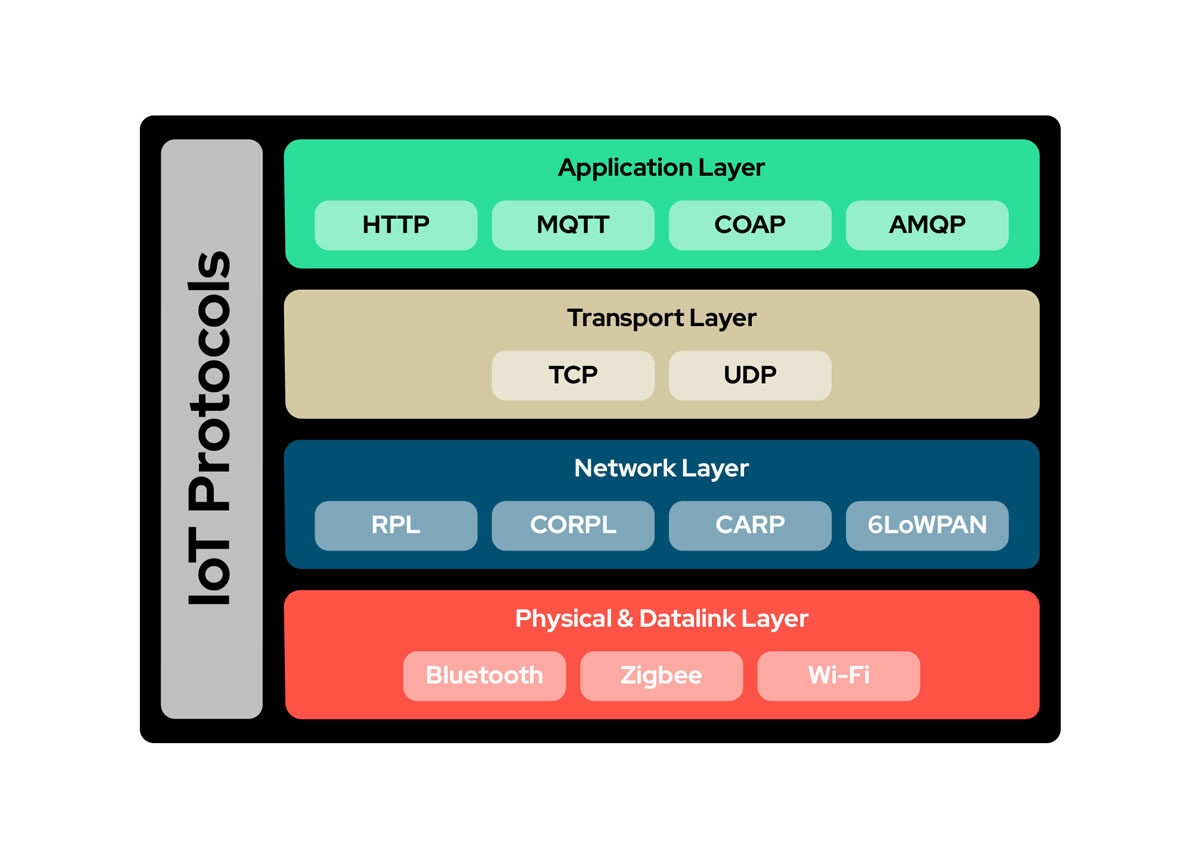
How IoT applications are transforming healthcare
Wearables for vital sign tracking
Wearable devices track real-time health metrics such as glucose, blood pressure, heart rate, and physical activity. Mobile apps collect data from these devices and transmit it to the cloud, where clinicians can analyze patient behavior and adjust treatment plans. Fitness bands and smartwatches are among the most popular consumer wearables that integrate with mobile applications.
Smart hospitals
Paperless hospitals and clinics use centralized electronic health records (EHRs) to manage patient data. Storing medical and billing records in cloud services makes them easier to access and manage. Smart hospitals gain benefits such as improved patient engagement, streamlined communication, hospital asset tracking, and optimized workflows.
Mobile health
Patient–clinician interactions are changing. Mobile health apps provide alternative ways to manage care. Telemedicine, telecare, and remote patient monitoring have been critical in emergent conditions such as asthma attacks, heart failure, and diabetes. Mobile health apps and connected devices are also used in clinical trials and in connected drug-delivery platforms.
Key benefits IoT delivers to healthcare
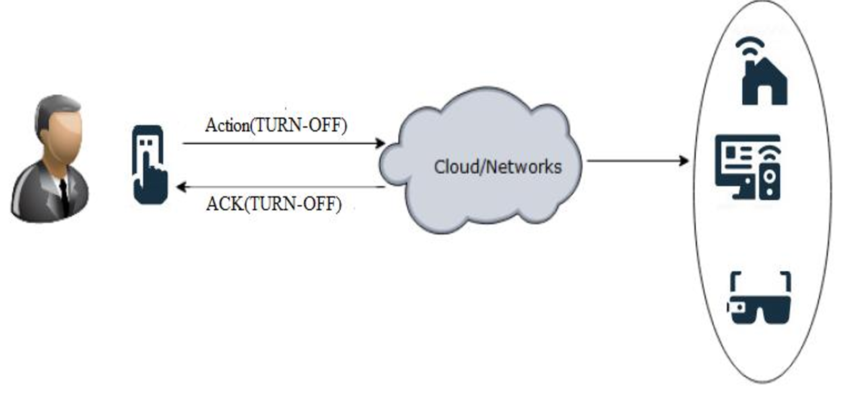
- Real-time monitoring – Connected medical devices provide personalized, real-time health status and can alert patients to check routine measures. In emergencies such as heart failure or asthma attacks, devices can notify clinicians and facilitate rapid contact.
- Improved patient experience – Connectivity between patients and healthcare systems increases engagement and gives clinicians access to real-time data that can improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Cost reduction – IoT solutions enable remote monitoring using real-time data, which can accelerate treatment, maintain ongoing communication, reduce hospital resource use, and lower travel-related expenses.
Challenges in adopting digital healthcare technologies
Digital healthcare systems that use IoT and big data create seamless digital connections with patients and increasingly integrate with various wearable devices to provide real-time information. However, several challenges must be addressed before broad adoption:
- Ensuring robust data security to maintain patient privacy.
- Integration complexity and slower data exchange caused by multiple devices using different protocols.
- Large data volumes require efficient storage and data management technologies.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB