Overview
In recent years, driven by infrastructure development, transformation of foundational industries, and consumption upgrades, sectors at different stages of development have alternately advanced the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), producing rapid global growth in the IoT industry. A report from Beizhes Information Consulting shows that in 2022 the global IoT market reached RMB 1,589.683 billion, while the Chinese market reached RMB 635.873 billion. The global IoT market is projected to grow to RMB 5,055.612 billion by 2028, with a 2022–2028 forecast CAGR of 21.34%.
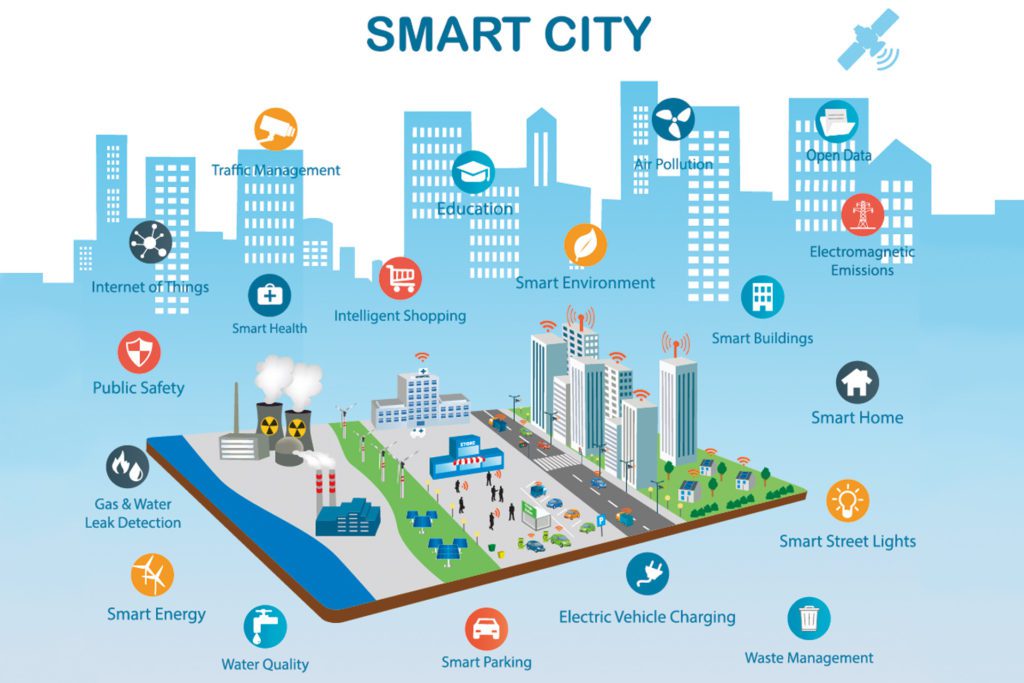
Large market demand is driving continuous iteration and innovation of IoT technologies, such as low latency, real-time information synchronization, and increased intelligence, accelerating digital transformation across industries and application scenarios. Smart cities, as a representative application area, rely on cloud computing and internet technologies to extend sensing and connectivity across urban infrastructure, while policy support and capital investment have also promoted deployments. IDC estimated that in 2023 global smart city technology-related investment would reach $189.46 billion, with the Chinese market reaching $38.92 billion. Under these conditions, infrastructure projects within cities are progressing steadily and industry players are offering solutions and operational experience that shape next-generation smart city models.
Integrated Smart Buildings: Energy Efficiency and Security
Energy efficiency and emissions reduction are central to smart city construction. Survey data indicate that urban populations account for about 55% of the global population, cities produce roughly 80% of global GDP, consume two thirds of total energy, and contribute more than 70% of annual global carbon emissions. With further urbanization, these figures are expected to increase. Buildings are a significant source of urban energy consumption; reducing energy waste while maintaining reliable building operation is a key industry challenge.
In traditional buildings, numerous systems and devices are often isolated, leading to low management efficiency, difficulty collecting data, and energy waste under conventional management approaches. As a result, developing efficient and sustainable building operation and management platforms has become a strategic objective for many organizations.
Schneider Electric has combined digital and electrical technologies with building management. Based on the EcoStruxure architecture and platform, a three-layer digital building solution comprising connected products, edge control, and applications, analytics, and services enables comprehensive management from planning and design through operation and maintenance. The platform aims to support accurate data acquisition, integrated operational display, precise control, and reliable operation and maintenance.
To address energy management for higher-value buildings, Schneider Electric released an energy efficiency management product called AIBOX (ShiHuineng). AIBOX supports digital twin modeling, validation, system tuning, and energy monitoring. Using digital twin modeling and dynamic simulation, it can provide optimized operation strategies for HVAC equipment and systems. By combining HVAC physical principles with machine learning-based gray-box models, the approach brings information technology capabilities to operational technology. AIBOX enables visualized analysis and control of building operation, quantifies energy-saving benefits, and supports gradual achievement of energy reduction and carbon goals.
Beyond energy efficiency, transforming buildings into environments that interact with occupants and adapt to their changing needs is another goal for intelligent buildings. Security is a typical application area for such interaction. Traditional building surveillance systems face challenges such as vast volumes of video data, slow manual review, and inflexible data access. Demand for intelligent upgrades to improve operational efficiency has increased.
Siemens worked with Jishijiao to develop a smart building management system to monitor dangerous people or objects around buildings and protect site security. Jishijiao developed algorithms for target recognition, virtual perimeter, people counting, and electric vehicle detection in elevator lobbies, and ported them to the Atlas 500 intelligent edge station. These AI capabilities augment Siemens Siveillance VMS with real-time detection and alerting of unsafe behaviors and states, helping to reduce safety risks and improve management efficiency.
By combining personnel, technology, and services, Siemens uses data and AI technologies to improve building performance. From intelligent video surveillance, identity management, intrusion and perimeter protection to electric vehicle controls in elevator lobbies, image and video collection plus data analysis speed response to hazardous events and provide decision makers with richer information for faster, more effective deployments while reducing manual labor and improving service levels.
Smart Transportation: Multi-Pronged Approaches to Mobility
Smart transportation is a core component of smart city infrastructure. With rising disposable incomes, vehicle ownership has increased, worsening urban congestion. As of March 2022, the total number of vehicles in China exceeded 400 million, exacerbating congestion. The move toward intelligent transportation systems has become necessary. The national digital transportation development plan sets targets for 2025, including broad coverage of digital sensing and information networks, intelligent and convenient transport services, coordinated online/offline governance, proactive technology application, and robust cybersecurity.
Urban road congestion, heavier holiday highway congestion, and suboptimal inland waterway utilization remain challenges. A Didi Chuxing urban travel report showed that in 2021 road congestion durations in China’s major cities often exceeded one hour, with peak road speeds below 40 km/h. Smart transportation technologies offer solutions to these problems.
In 2023, Huawei launched the AI Ultra-Low-Light 3.0 camera series for smart traffic management. Using an ISP4CAR algorithm combined with AI pixel-level segmentation and AI ISP techniques, the cameras aim to prevent license plate overexposure, reduce artifact duplication from vehicle windows, restore true vehicle colors, and clarify in-cabin targets, improving imaging across scenarios by combining optical and computational imaging.
Camera systems for checkpoint scenarios meet GA/T1202-2022 Class 1 auxiliary lighting standards, enabling effective nighttime capture under illuminance below 80 lx. The AI ultra-low-light series of traffic enforcement cameras can operate without external fill lights in scenes above 10 lx, reducing infrastructure costs and saving energy. The ITS800 edge device and binocular radar-vision integrated unit support diverse applications, improving traffic governance efficiency. Huawei’s SuperFusion perception fusion technology integrates radar and vision to accurately characterize each intersection, lane, and vehicle behavior, improving accuracy and deployment ease.
Public transit also faces growing passenger volumes. Infineon has addressed fare system modernization by introducing the CALYPSO move secure element, enabling contactless ticketing solutions that comply with the Calypso base specification. The open-standard secure element avoids vendor lock-in, supports low-cost paper-ticket implementations while meeting transit and access security requirements, and is compatible with existing Calypso automatic fare collection systems. It is certified to Common Criteria EAL2+ standards for enhanced basic assurance, offering improved security and strong contactless performance for limited-lifespan tickets.
Advancing Energy Storage Digitization to Stabilize Power Supply
Urban smart development depends on resilient power systems. Since national planning initiatives, ensuring long-duration power supply from new energy sources within urban areas remains a challenge. Frequent load-shedding in some resource-constrained cities and supply uncertainty in resource-supplying cities have created notable supply-demand gaps. Energy storage, by improving supply reliability and flexibility, is an effective approach to address these issues.
In high-voltage storage battery environments, voltage stability, charge-discharge stability, and thermal management are critical. Accurate battery state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) estimation can extend battery life by 10 to 20 years. Battery management systems (BMS) play a central role, precisely measuring module-level data and system temperatures, which are essential for safe charging, discharging, and monitoring.
Analog Devices (ADI) introduced the AD BMS1818, an 18-channel high-precision battery management chip optimized for industrial energy storage. As a multi-cell battery stack monitor, ADBMS1818 measures up to 18 series-connected cells with a 0–5 V input range and a total measurement error under 3.0 mV, suitable for most chemistries. It can measure all 18 cells within 290 μs, enabling support for 50 V battery modules on a single chip. Multiple ADBMS1818 devices can be cascaded to monitor very long high-voltage strings. To reduce system noise before it affects BMS performance, the device integrates a 16-bit sigma-delta ADC and includes programmable noise filters to mitigate electromagnetic interference and transient noise.
For conversion between new energy sources and storage, high-power switching components and controllers are required. STMicroelectronics provides a broad product portfolio, including GaN and SiC-based solutions, fast shutdown chips, high-voltage MOSFETs, IGBTs, power modules, STM32 G4 microcontrollers, and related power management devices. These components aim to enable efficient, high-performance energy conversion solutions. At the same time, as large-scale energy storage projects are commissioned, ensuring intrinsic safety of high-capacity storage batteries has become critical. In the past decade there have been over 60 reported energy storage safety incidents, with 18 since 2021. Battery stacks, cells, and modules at storage sites can each be sources of incidents, so improving energy conversion efficiency, intrinsic safety, and operational safety management is necessary to enhance the economic viability and quality of modern energy storage systems and electronic systems.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things provides a technical foundation for smart cities, enhancing urban sensing capabilities and making perception deeper and more intelligent. Through environmental sensing, urban infrastructure monitoring, personal health sensing, and interactive perception in intelligent transportation, smart cities can support intelligent management across municipal services, public welfare, and industry. In this context, smart cities are a primary target for IoT applications, and IoT technologies act as accelerators for urban development.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB