Smartwatch features and uses
Smartwatches offer multiple functions and uses. Below are some common features and applications:
- Time display: The basic function is to show the current time, date, and related information.
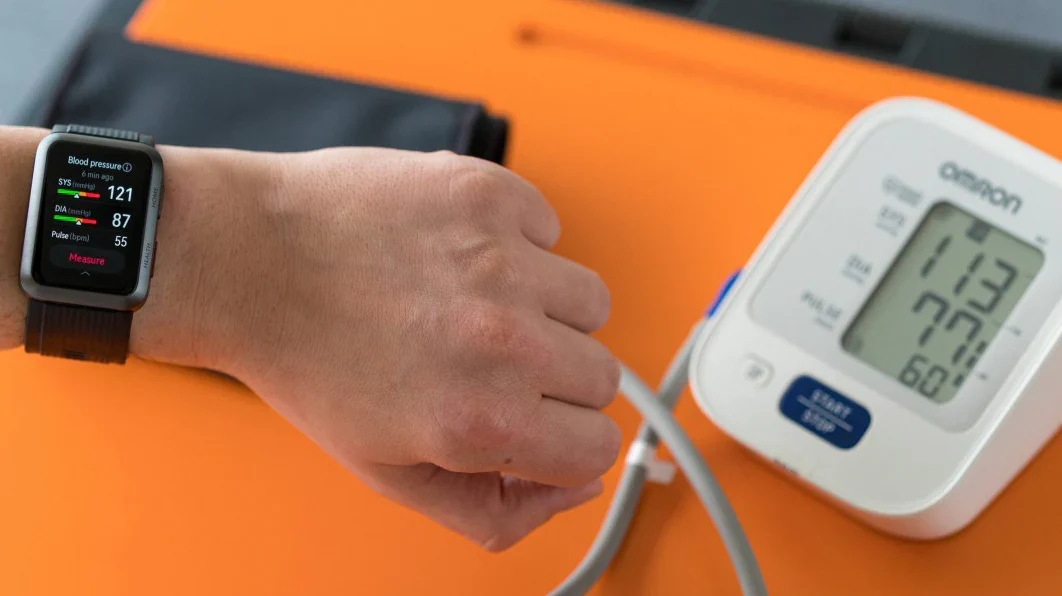
- Health monitoring: Smartwatches typically include various sensors that can monitor heart rate, blood pressure, sleep quality, and other health indicators in real time to help users understand and manage their health.
- Activity tracking: Smartwatches can record activity data such as step count, distance, and calories burned. They often provide exercise mode selection and GPS functionality to support running, cycling, swimming, and other activities while monitoring performance.
- Notification alerts: When connected to a phone, a smartwatch can notify the user of incoming calls, text messages, and social media messages via vibration or on-screen alerts, reducing the need to take out the phone frequently.
- App support: Smartwatches can run various applications such as weather, calendar, music playback, and navigation to provide additional practical functions and services.
- Contactless payment: Some smartwatches support NFC for contactless payments, enabling convenient transactions.
- Emergency call: Some models include an emergency call feature that allows the user to send help messages or place a call to emergency contacts.
- Customizable watch faces and styles: Many smartwatches offer a range of watch faces and display styles that users can change to match personal preferences.
Note that features and capabilities vary by brand and model; refer to the product's actual supported features. Smartwatch functions continue to evolve and may see further improvements.
Can smartwatches measure blood pressure accurately?
Smartwatch blood pressure monitoring generally estimates blood pressure by using optical sensors to detect pulse waveforms and applying algorithms to infer approximate blood pressure values. Currently, most smartwatches' blood pressure functions are intended for reference only. Their accuracy is limited and they should not replace professional medical devices for precise blood pressure measurement.
This limitation stems from the fact that optical sensors estimate blood flow at the skin surface and are affected by many factors and interferences, such as the wearing position, device quality, strap tightness, and distance from the heart. Individual physiological differences, activity level, and ambient temperature can also affect measurements.
Therefore, for accurate blood pressure measurement, use a medical-grade blood pressure monitor and perform measurements under professional guidance. Smartwatch blood pressure readings can serve as a reference but should not be relied upon exclusively to assess health.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB