What is a head-mounted display
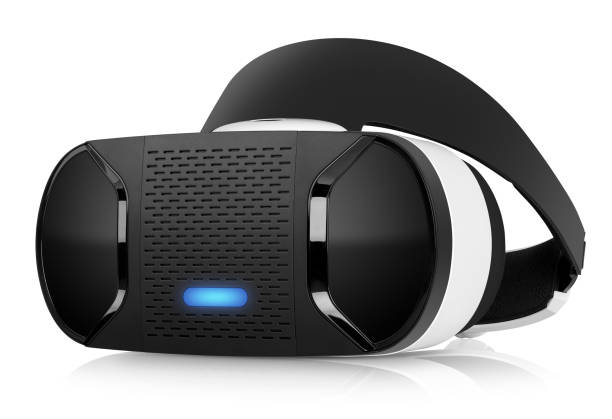
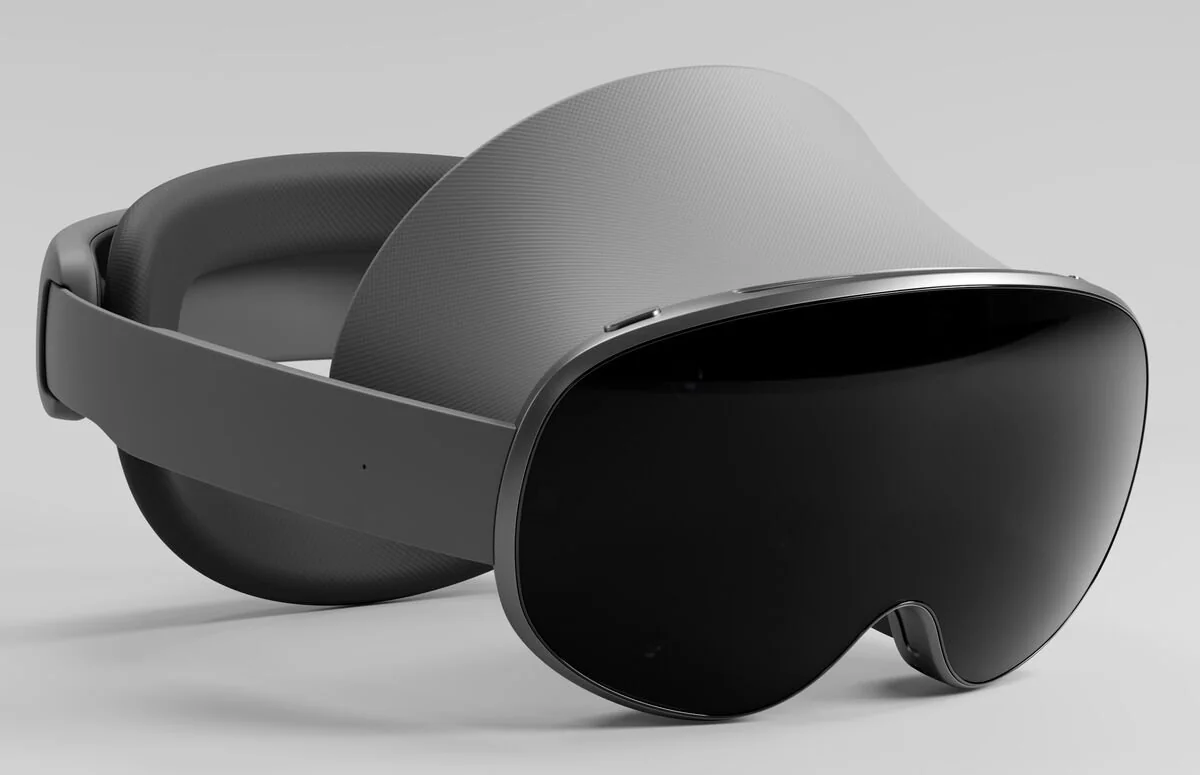
A head-mounted display (HMD) is a wearable display device worn on the head, typically in the form of glasses, a helmet, or a headband. It places a screen directly in front of the user's eyes to present virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), or mixed reality (MR) content.
Common characteristics of HMDs include:
- Display technology: HMDs use high-resolution displays or optical projection systems to present images or video and provide an immersive visual experience. Typical display technologies include liquid crystal display (LCD) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED).
- Head tracking: To provide realistic and interactive experiences, HMDs usually integrate sensors to track head movements and adjust the perspective and position of displayed content in real time.
- Interaction methods: HMDs are commonly equipped with buttons, touchpads, controllers, or gesture recognition, allowing users to interact with virtual environments and control applications.
- Audio output: To enhance immersion, HMDs often include audio output such as stereo headphones or speakers, providing a more realistic sound experience.
HMDs are used in VR gaming, training and simulation, healthcare, design and engineering, and other fields. By wearing an HMD, users can be immersed in virtual environments and interact with simulated elements.
Do head-mounted displays harm the eyes?
Extended use of HMDs can affect the eyes to some degree, but not everyone will experience the same effects. Common eye-related issues and recommendations include:
- Fatigue and discomfort: Prolonged focus on a screen can cause eye fatigue, dryness, and blurred vision. It is advisable to take regular breaks, look at distant objects, and perform eye relaxation exercises.
- Blue light exposure: HMDs emit blue light, and long-term exposure to high-intensity blue light may have cumulative effects. Options to reduce exposure include wearing blue-light-filtering glasses, using blue-light filters, or adjusting the display color temperature.
- Vision development concerns: Excessive use of HMDs over long periods may increase the risk of myopia, particularly in children and adolescents. Limit usage time, maintain proper posture and viewing distance, and have regular eye examinations.
Advantages and disadvantages of head-mounted displays
Head-mounted displays have several advantages and disadvantages. The most common ones are listed below.
Advantages:
- Immersive experience: HMDs can provide a highly immersive experience, making users feel present in the virtual environment, which is particularly suitable for VR applications.
- Privacy: With the display positioned directly in front of the eyes, HMDs can isolate the user from the external environment and offer a more private experience.
- Interactivity: HMDs typically support multiple interaction methods, such as controllers, touchpads, and gesture recognition, enabling users to interact with virtual content.
- Portability: Compared with large traditional displays, many HMDs are relatively lightweight and allow users to more easily access VR or AR content.
Disadvantages:
- Visual fatigue: Prolonged use may cause eye fatigue, dryness, and related discomfort, so users should take breaks and protect their eyes.
- Discomfort with extended wear: Because the device is worn on the head, some users may experience discomfort or pressure, especially during long sessions.
- Dependence on external hardware: Many HMDs require connection to a PC, game console, or other devices to function, which can add complexity and usage constraints for some users.
- Cost: Some high-end HMDs are expensive and may not fit all budgets.
Note that as technology advances, the advantages and disadvantages of HMDs may change. Before purchasing, it is advisable to research and compare products to determine whether a given HMD meets individual needs and expectations.
 ALLPCB
ALLPCB